Video Link
https://www.educator.com/economics/ap-microeconomics/park/
Table of Contents
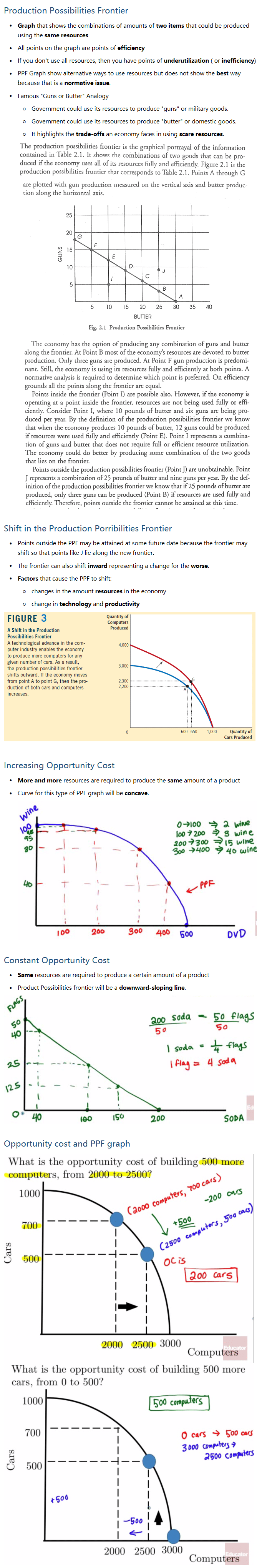
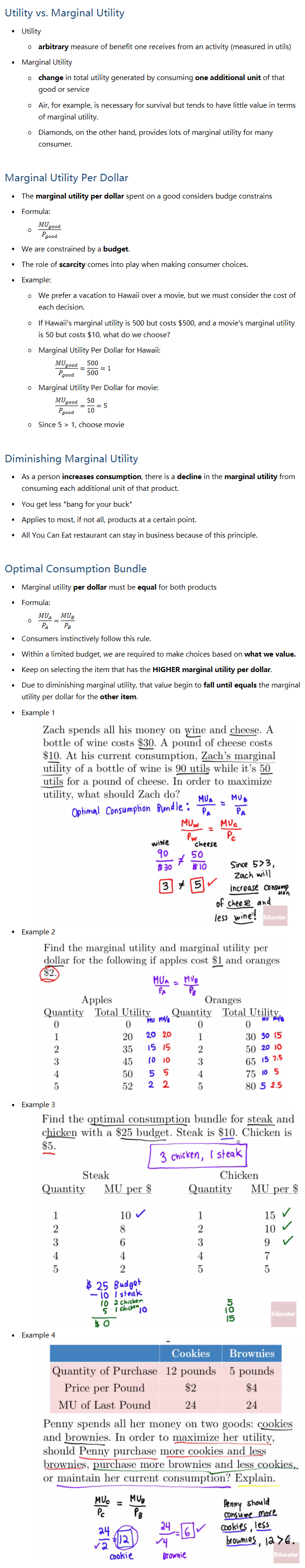
1.2 - Producton Possibilities Frontier
1.3 - Comparative Advantage & Trade
2.4 - Price lasticity of Demand
2.5 - Income, Cross-Pric & Supply Elasticities
2.6 - Total Surplus, Deadweight Loss & World Trade
2.7 - Production Function & Firm Costs
2.8 - Long-Run Costs & Economies of Scae
3.3 - Monopoly & Public Policy
3.5 - Monopolistic Competition
4.2 - Laor Supply & Cost Minimization
5.1 - Positive & Negative Externalities